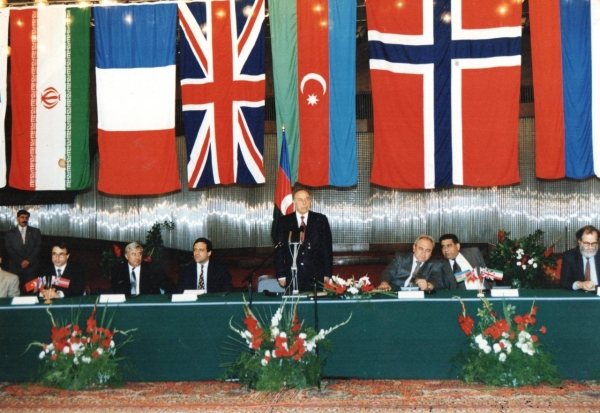
Unique not only from the geopolitical, economic and commercial but also from the legal standpoint ((there has not been such a form of agreement adopted in world practice within the former USSR), and having passed through all obstacles and stages of approval, the agreement on the joint development and production sharing for the Azeri and Chirag fields and the deep water portion of the Gunashli field was signed with the participation of 12 companies from 8 countries under the leadership of the National Leader of Azerbaijan Heydar Aliyev in Baku on September 1994. The contract was ratified by Milli Majlis on December 12, 1994. The first composition of the then Consortium was as follows: BP/Amoco plc.(Great Britain-USA) – 34.1267%, Exxon – 8.00006%, Pennzoil -4.8175%, Unocal -10.0489, Ramco – 2.0825%, Statoil -8.5633, Itochu – 3.9205, LUKOIL - 10%, SOCAR-10%, TPAO – 6.8, Delta – 1.68%.
Over 14 PSAs were signed further for performing offshore operations. Among them are the Shah Deniz and Absheron gas condensate fields.
It is noteworthy that this contract was signed twice - for the second time the updated agreement envisaging the development of fields till the end of 2049 was signed by the Azerbaijan President Ilham Aliyev on September 14, 2017. In the course of time, the share participation scheme in the contract underwent changes aside one time. Now, 30 years later, it still remains a world class project. The current share participation in the ACG project is as follows: bp (30.37%), SOCAR (25.0%), MOL (9.57%), INPEX (9.31%), Equinor (7.27%), ExxonMobil (6.79%), TPAO (5.73%), ITOCHU (3.65%), ONGCVidesh (2.31%).
Following the contract term extension, a decision to implement another new project on construction of the $6 billion Azeri Central-East (ACE) platform was made on April 19, 2019. It was another step in the development of ACG. ACE produced first oil on April 16, 2024.
At the end of the second quarter of 2024, capital expenditures on the development of the Azeri-Chirag-Gunashli (ACG) block of fields in the Azeri sector of the Caspian Sea totaled $45 billion.
From the start of production at ACG in November 1997 until the end of the second quarter of 2024, 593 million tons (approximately 4.4 billion barrels) of oil were produced from ACG, ‘Respublika’ reports with reference to the field operator bp-Azerbaijan.
From the start of production until the end of the second quarter of 2024, approximately 57 billion cubic meters of associated gas from ACG were delivered to Azerbaijan.
Since the ACG project started in 1994, BP and its partners have allocated about $111 million for the implementation of social projects in Azerbaijan.
At the end of the second quarter of 2024, operating at ACG were 144 production, 45 water injection and 8 gas injection wells.
As reported on the website of the Heydar Aliyev Foundation, this contract became a turning point in the oil industry of Azerbaijan, which has a 150-year history, and the beginning of the implementation of the oil strategy in the newly independent Republic of Azerbaijan. Entering history as "the Contract of the Century", this international oil project was of exceptional importance in the protection and strengthening the independence of Azerbaijan.
The Contract of the Century laid the foundation for the implementation of other major projects in Azerbaijan. By implementing these projects, Azerbaijan found more reliable political and economic partners and allies across the world. Other areas of the Azerbaijani economy also witnessed the increase in the inflow of foreign investments after the signing of the contract. Right after signing of the Contract of the Century, concluded were 27 oil contracts with 43 companies from 21 countries, which envisaged investments worth $60 billion into the development of Azerbaijan’s oil industry (http://www.socar.gov.az/).
Following the signing of the Contract of the Century, in parallel with the continuation of negotiations on the contract, key operational bodies such as the Steering Committee, Azerbaijan International Operating Company (AIOC) and the Advisory Council were established. Azerbaijan President’s special decree dated December 2, 1994 made the activity of those structures legally binding.
Bp has been a single operator of AIOC since June 1999. The work program and budget for special projects of the AIOC are approved by SOCAR, the Azerbaijani government and the Steering Committee consisting of representatives of foreign oil companies.
Early oil production within the framework of the Contract of the Century began in November 1997, and based on the results of the year 2007, the production performance witnessed a monthly and annual increase within the framework of the project. For instance, Azerbaijan produced a record volume of 42.6 million tons of crude oil in 2007. Of that volume, SOCAR and international consortiums accounted for 8.8 million and 33.8 million tons, respectively. Compared to 2006, oil production rose by 33%, that is to say, by 10.3 million tonshttp://www.azerbaijan.com/).
In 2004, the parties to the Contract of the Century were bp-34.14% (Great Britain), Unocal-10.28% (USA), SOCAR -10% (Azerbaijan), Inpex-10% (Japan), Satoil-8.56% (Norway), ExxoMobil -8% (USA), TPAO -6.75% (Turkiye), Devon-5.63% (USA), Itochu -3.92% (Japan), Delta Hess-2.72% (Saudi Arabia).
In 2002, the company LUKoil representing Russian in the consortium sold its 10% stake in the contract to the Japanese company INPEX for $1.375 billion.
The Baku-Novorossiysk and Baku-Supsa pipelines with a capacity of 5-7 million tons of oil per year were used until mid-2006 to export Azerbaijani oil to world markets. Nevertheless, in order to bring annual production at Azeri-Chirag-Gunashli to 50 million tons and deliver that oil to world oil markets, President of the Azerbaijan Republic Heydar Aliyev proposed to consider a new export pipeline project possessing a much broader carrying capacity. In 1998, the route of the main export pipeline Baku-Tbilisi-Ceyhan (BTC) was chosen as a profitable option. In September 2002, an oil pipeline foundation laying ceremony was held in Baku. In May 2006, the transportation of early Azerbaijani oil through the BTC pipeline began, which contributed to the accelerated development of the Azerbaijani economy. Considering the indispensable role that Heydar Aliyev played in the implementation of this project, the shareholders decided to name the BTC pipeline after him in 2004.
Since 2007, the Republic of Azerbaijan has begun to implement the policy of entering the global energy market not only as an exporter of crude oil, but also as a supplier of finished oil products. Thus, in 2007, Azerbaijani refineries processed 7 million 504 thousand tons of oil. And this is 0.7% or 53.4 thousand tons more than the annual figure in 2006. Construction of a new oil refinery with a capacity of 200 thousand barrels began in the Turkish port of Ceyhan on the Mediterranean Sea, where Azerbaijani crude oil is delivered in large volumes. In spring of 2008, the Kulevi terminal belonging to the Republic of Azerbaijan was also launched in Georgia (http://www.socar.gov.az/).
The relevant infrastructure of Azerbaijan is very advantageous for the transportation of oil and natural gas from Central Asia to Europe. SOCAR is one of the active participants of "Sarmatia" international pipeline company established with the aim to lay Odessa-Brody oil pipeline toward Plock (http://www.azerbaijan.com/).
At the signing ceremony of the "Contract of the Century," President of the Azerbaijan Republic Heydar Aliyev in his high estimation of the event said in his extensive speech: “I am happy to have participated in the drawing up and signing of this contract. I realise my responsibility and I am hopeful that future generations will appreciate today`s historic event.” In the next three years, Azerbaijan's oil and gas revenues are expected to decrease amid rising non—oil and gas revenues, the country's oil and gas revenues in 2024 will amount to 17.769 billion manats, in 2025 - 17.073 billion manats, and by 2028 they will decrease to 15.761 billion manats. Thus, by 2028, oil and gas revenues will decrease by 11.3% (by 2.007 billion manats) compared to 2024. This is reflected in the parameters of the consolidated and state budget for the year 2025 and subsequent years, published by the Ministry of Finance.
At the same time, non-oil and gas revenues will grow. In 2024, their volume will amount to 18.619 billion manats, in 2025 — 19.543 billion manats. By 2028, it is projected to increase to 23.992 billion manats. This is more than 28.8% growth (by 5.373 billion manats) compared to 2024. Thus, the growth of Azerbaijan's non-oil and gas revenues will exceed 28%.
On December 17, 2022, the governments of Azerbaijan, Georgia, Romania and Hungary signed an agreement on strategic cooperation in the field of development and transfer of green energy. One of the important points of the agreement was the Black Sea submarine cable project. Once implemented, a 1,195 km long cable (1,100km – subwater, 95km – onshore) will be linked to Romania. This will enable European countries to transport 4 GW of green energy from Azerbaijan.
Important MoUs and agreements signed by Azerbaijan with international companies will allow us to produce up to 22 gigawatts of wind and solar energy.
“Today Azerbaijan not only satisfies all its needs with energy but also exports crude oil, oil products, natural gas, petrochemicals, and electricity. Our program with respect to renewables has an entirely different agenda. Firstly, this sector has enormous potential. Secondly, it will help us to diversify our export and, of course, create a new ecologically-friendly sector of our economy”, President of Azerbaijan said.
The investment climate in Azerbaijan is very positive, and we accumulated considerable investments in the oil and gas sector. But now our target is renewables. So, in other words, we have great plans. According to President Ilham Aliyev’s order signed on September 19, 2024, September 20 will be annually celebrated as the State Sovereignty Day in the Azerbaijan Republic.